Prevention and Recovery from Blood Clots: A Comprehensive Biological Approach
Blood clots are a silent threat that doesn't discriminate based on fitness level or lifestyle. They can arise without warning and have devastating consequences, from strokes to deep vein thrombosis. Conventional solutions often focus on managing symptoms or preventing new clots, but rarely address the biological root of the problem. This article delves into a comprehensive protocol designed to dismantle existing clots, repair damaged vascular linings, and restore blood chemistry to an anti-inflammatory state, using molecular tools the body already understands and has evolved to use. The mission is to empower the body to heal itself, rather than simply managing disease.
1. Introduction: The Silent Threat of Blood Clots
Blood clots pose a significant health risk, which can manifest in a variety of ways, from tingling in the hands and feet to swelling, leg pain, or a feeling of pressure under the ribs. These signs, often dismissed by conventional medical tests, can indicate an underlying problem that, if left unaddressed, could lead to serious events such as stroke, portal vein thrombosis, or pulmonary embolism. The body's internal biology, if compromised, can turn anyone into a silent "ticking time bomb," regardless of their physical appearance. This article proposes a detailed molecular strategy to dismantle clots, repair damaged blood vessels, and restore an anti-inflammatory balance, offering a proactive option beyond simply managing symptoms.
2. Understanding the Coagulation Mechanism: Survival vs. Pathology
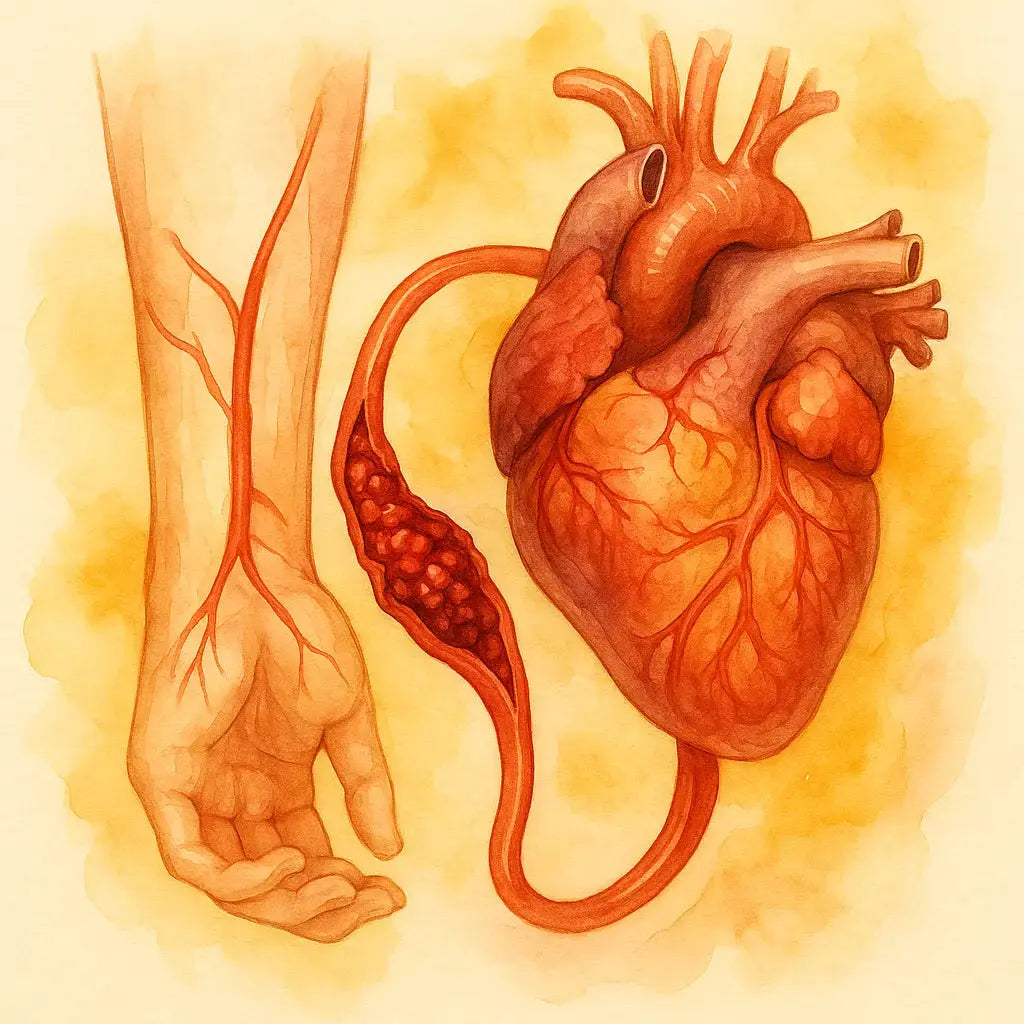
A blood clot, in essence, is not the villain; it is a crucial survival mechanism of the body. If the body could not form clots (as in hemophilia), a small wound could be fatal. Clotting is the body's natural way of "patching" what it perceives as a threat. This occurs when the inner lining of blood vessels, called the endothelium, suffers some kind of damage, inflammation, or trauma.
In response, the body releases a "band-aid" made of platelets and fibrin, triggering a cascade of coagulation signals to "plug the hole" and prevent the loss of vital fluids. The problem arises when the underlying signal of damage or inflammation is never resolved. The body continues to form these small "plugs" which, over time, accumulate and become blockages, leading to dangerous conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism, stroke, or heart attack. Factors such as chronic inflammation, autoimmune dysfunction, or interference from the spike protein can predispose the body to form clots excessively.
3. The Limitations of Conventional Treatments
When a patient arrives at a hospital with a blood clot, the standard treatment is anticoagulants, such as heparin, enoxaparin, or warfarin (rat poison). The logic is simple: more diluted blood cannot clot. However, this approach has significant limitations:
- They Do Not Dissolve Existing Clots: Anticoagulants only prevent the formation of new clots; they do not dissolve those that are already present. It's like trying to stop a basement flood by turning off the sink faucet: it doesn't address the water that's already there.
- They Increase the Risk of Bleeding: By interfering with the body's natural ability to clot, anticoagulants increase the risk of internal bleeding, nosebleeds, or complications during minor surgeries. This can put the patient in danger, as it eliminates the body's ability to respond to bleeding emergencies.
- They Don't Address the Root Cause: These drugs don't resolve the underlying inflammation, fibrin overproduction, or ongoing endothelial damage that triggers clot formation in the first place. Current medical care often focuses on managing problems, not creating lasting solutions.
If a problem requires ongoing medication, it means the root cause hasn't been addressed. The smartest approach is to help the body dissolve existing clots, rebuild damaged vascular lining, and extinguish the inflammatory fire that triggers these biological panic attacks.
4. The Comprehensive Biological Protocol: A Molecular Strategy
This protocol represents a "dream team" of compounds that work in concert to dismantle clots, repair vessels, and restore blood chemistry from a pro-thrombotic to an anti-inflammatory state. These are not pharmaceuticals, but rather enzymes, peptides, and growth signals that the body already understands and has used throughout its evolution.
4.1 Pillar 1: Lumbrokinase - The Precision Fibrin Solvent
Lumbrokinase is an enzyme derived from earthworms that acts like a "sniper" against fibrin. Fibrin is the sticky protein that holds blood clots together. Unlike anticoagulants, lumbrokinase does not thin the blood or increase the risk of bleeding. Instead, it activates plasmin, an enzyme that dissolves the clot safely and precisely, like Pac-Man on "trick mode."
4.2 Pillar 2: Serrapeptase and Nattokinase - The Cleaning and Demolition Team
These two compounds work together like a biological cleanup and demolition team. Serrapeptase removes biofilm, old scar tissue, and fibrin that shouldn't be there, acting like a "biological vacuum cleaner." Nattokinase, although slower than lumbrokinase, also supports the clot-dissolving process, acting as an effective complement. Their combination is crucial, since the body functions like a "team sport," and better results are achieved by utilizing all the "players."
4.3 Pillar 3: BPC-157 - The Master of Vascular Repair
BPC-157 is a peptide known as the "body protection compound" and is remarkable for blood vessel repair. It acts as the "ultimate contractor" for endothelial cells, where clots form. It repairs the endothelial lining, reduces inflammation (especially in the liver's portal vein, a high-risk area), and promotes angiogenesis—the formation of new blood vessels in cases of obstruction—to ensure oxygen perfusion to tissues.
4.4 Pillar 4: TB-500 - Restoration of Vascular Elasticity and Connective Tissue
Blood clots not only dissolve, but often leave behind scar tissue, fibrosis, and a loss of flexibility in the blood vessels, compromising their elastic function. TB-500 is key to breaking down this scar tissue and restoring blood vessel flexibility, which is vital for a healthy vascular system. Furthermore, it improves circulation by restoring actin regulation in the vascular wall, a crucial process for cell movement to injured areas.
4.5 Pillar 5: GHK-Cu - The Vascular Anti-inflammatory and Capillary Regenerator
GHK-Cu (copper peptide) is a potent anti-inflammatory that plays a crucial role in vascular health. It massively increases Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF), which supports nitric oxide for vasodilation and regenerates the small networks of blood vessels that may be damaged or absent. This is especially important in the gut and liver, where oxygen perfusion is critical for optimal function. It acts like an "adamantium" armor around neurons, protecting the entire system.
4.6 Pillar 6: MK-677 - Tissue Regeneration Accelerator
MK-677 is a growth hormone (GH) secretagogue, meaning it stimulates the body to naturally produce more GH and IGF-1. By increasing these factors, tissue regeneration is accelerated to optimal levels without stressing the system. This is crucial for the recovery of endothelial cells, hepatocytes (liver cells), and vascular smooth muscle. It is a key factor in cell regeneration, with a very high return on investment in recovery.
4.7 Pillar 7: TUDCA and NAC - Liver Protection and Cellular Detoxification
These compounds, while not as "attractive," are vital, especially for protecting the liver, one of the organs most affected by thrombotic events such as portal vein thrombosis. TUDCA (tauroursodeoxycholic acid) and NAC (N-acetylcysteine) support bile flow, reduce endoplasmic reticulum stress in the liver, and increase the production of glutathione, the body's master antioxidant. They are essential for protecting the liver from the devastating consequences of thrombosis and oxidative stress.
4.8 Pillar 8: Epitalone - The Anti-Aging Genetic Reset
Epitalon is a massive genetic reset button. It helps prevent recurrent blood clots by addressing telomere shortening and mitochondrial dysfunction, which are key factors in aging and clotting predisposition. It works at the genetic level, reversing the aging of the vascular system and restoring its optimal function. It's like flipping the switch on vascular aging, causing it to operate like a younger, healthier system.
5. Post-Vaccination Considerations: Addressing Spike Protein Interference
It is a well-established fact that the spike protein in mRNA-based vaccines has been implicated in disrupting endothelial function, microclot formation, increased platelet activation, and reduced mitochondrial integrity. For those who have experienced clotting symptoms after vaccination, this protocol is not a political statement, but a molecular strategy to address the biological consequences of this interference.
The combination of lumbrokinase, nattokinase, and serrapeptase safely and precisely dissolves fibrin without compromising the body's natural emergency clotting ability. BPC-157, TB-500, and GHK-Cu, the "Wolverine protocol," rebuild the vasculature, expand microvessels, and reduce overall inflammation. MK-677 and Epitalon accelerate cellular recovery, enhance cell signaling, and repair genetic damage (including telomeres). Finally, TUDCA and NAC protect the liver and blood from oxidative stress and an overactive immune system. This approach is not for symptom management, but for deep cellular reconstruction.
6. Who is this protocol for, and who is it not for?
This hypothetical protocol is designed for individuals (or "mice", in the experimental context) who:
- They are prone to blood clot formation (post-surgical, post-vaccination, etc.).
- They have been diagnosed with DVT, PBT, or unexplained vascular inflammation.
- They experience chronic inflammation, swelling, or a hyperreactive system.
For these individuals, this protocol offers a roadmap to "repair the machine" at a biological level. However, it is not for those seeking an "effortless miracle." It requires rigorous daily discipline and consistent blood monitoring (complete blood count, fibrinogen, D-dimer). It is crucial to understand that this is not FDA-approved medical advice, but rather educational information. A blood clot cannot be resolved by waiting, ignoring swelling, or taking aspirin as a universal solution. Biology responds to the right signals, and this protocol is designed to give those signals to the body so it can repair itself.
Dosage Protocol: Prevention and Recovery of Blood Clots - Comprehensive Molecular Strategy
IMPORTANT: General Usage Considerations
Blood clots represent a silent threat that can manifest as anything from tingling in the hands/feet, swelling, and leg pain to a feeling of pressure under the ribs—signs frequently dismissed by conventional medical tests that may indicate an underlying problem which, if left unaddressed, could lead to serious events (stroke, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, portal vein thrombosis). A clot, in essence, is not a villain but a crucial survival mechanism—the body forms clots using platelets and fibrin like a "band-aid" when the endothelium (inner lining of blood vessels) is damaged, inflamed, or traumatized. The problem arises when the underlying signal of damage/inflammation is never resolved—the body continues to form "plugs" that accumulate, becoming dangerous blockages (DVT, pulmonary embolism, stroke, heart attack), particularly when there are predisposing factors such as chronic inflammation, autoimmune dysfunction, or spike protein interference. Conventional treatments FAIL because anticoagulants (heparin, warfarin, enoxaparin) only prevent the formation of NEW clots but DO NOT dissolve existing ones - it's like "stopping a flood by turning off the tap without addressing the water that's already there", they increase the risk of bleeding (they nullify the natural ability to clot), and they DO NOT address the root cause (inflammation, overproduction of fibrin, continuous endothelial damage that triggers clotting) - if the problem requires continuous medication, it means that the root cause has NOT been resolved. This comprehensive protocol represents a "dream team" of compounds working in concert to: 1) Dismantle existing clots (Lumbrokinase as the "sniper" activating plasmin to dissolve fibrin without diluting blood, Serrapeptase/Nattokinase as the cleanup crew removing biofilm/scar tissue/fibrin), 2) Repair damaged vessels and endothelium (BPC-157 as the "ultimate contractor" repairing endothelial cells where clots form, TB-500 restoring vascular elasticity and dismantling post-clot fibrosis, GHK-Cu as a potent anti-inflammatory regenerating capillaries via VEGF/nitric oxide), 3) Accelerate tissue regeneration (MK-677 stimulating endogenous GH/IGF-1 for endothelium/hepatocyte/vascular smooth muscle recovery), 4) Protect the liver from thrombosis (TUDCA/NAC supporting bile flow, reducing stress on the liver). endoplasmic reticulum, increasing glutathione), and 5) Anti-aging genetic reset (Epitalon preventing recurrent clots by addressing telomere shortening and mitochondrial dysfunction). CRITICAL: This protocol is NOT symptom management but deep cellular reconstruction that requires rigorous daily discipline and constant blood monitoring (complete blood count, fibrinogen, D-dimer) - it does NOT replace medical evaluation in acute events requiring immediate intervention. The protocol is implemented in phases: Phase 1 Intensive (first 4-8 weeks with full stack for aggressive dissolution + repair), Phase 2 Consolidation (weeks 8-12 reducing fibrinolytic enzymes while maintaining repairers), Phase 3 Maintenance/Prevention (long-term intermittent use). The fundamentals of a natural anticoagulant anti-inflammatory diet (rich in omega-3, garlic, turmeric, ginger, elimination of processed sugars/oils), optimal hydration (2-3 liters of water daily), regular movement (avoid prolonged sedentary behavior), and inflammation management are absolutely non-negotiable.
PILLAR 1: Precision Fibrin Solvent - Anticoagulant Sniper
Lumbrokinase
• Dosage : As an earthworm-derived enzyme that acts as a "sniper" against fibrin (the sticky protein that holds clots together) by activating plasmin (an enzyme that safely and precisely dissolves clots like "Pac-Man on trick mode") WITHOUT thinning the blood or increasing the risk of bleeding, unlike pharmaceutical anticoagulants, lumbrokinase is crucial because it dissolves EXISTING clots and not just prevents new ones. In the context of established clots (DVT, portal vein thrombosis, post-vaccination microclots, high thrombotic risk) where targeted and safe fibrinolysis is required, a dose of 20-40 mg of active lumbrokinase per administration is recommended (typically equivalent to 1-2 capsules of standardized products containing 20 mg of active enzyme per capsule). For prevention in high-risk individuals (post-surgical, history of DVT, antiphospholipid syndrome, prolonged immobilization), 20 mg (1 capsule) twice daily may be appropriate. For aggressive dissolution of established clots or disseminated microclots, 40 mg (2 capsules) two or three times daily provides more robust fibrinolytic activity. CRITICAL : Lumbrokinase must be taken STRICTLY on an empty stomach (fasting) because the presence of food dramatically inactivates the proteolytic enzymes—take 60+ minutes before a meal or 2–3 hours after the last meal.
• Administration Frequency : Lumbrokinase is administered orally in enteric-coated capsules (coated to resist stomach acid and release enzymes in the intestine where they are absorbed), typically two or three times daily on an empty stomach. Standard Aggressive Dissolution Protocol : First dose upon waking (6-8 AM) 60+ minutes before breakfast, second dose mid-afternoon (3-4 PM) between meals, third dose at night (9-10 PM) 3+ hours post-dinner before bed. Maintenance/Prevention Protocol : Two daily doses (morning fasting + night pre-sleep) may be sufficient once the acute risk has passed. Timing while fasting is absolutely critical—even a small amount of protein in the stomach (coffee with milk, snack) can neutralize 70-80% of enzyme activity. Many users set alarms to ensure correct timing. Absolute consistency in timing and fasting status maximizes effectiveness.
• Cycle duration : Lumbrokinase can be used for 8-12 week cycles as an intensive dissolution phase for established clots or microclots. During this period, progressive improvements are observed in: reduction of clot symptoms (swelling, pain, and pressure typically decrease dramatically within 2-4 weeks), normalization of coagulation markers (D-dimer, which measures fibrin degradation products, should decrease toward the normal range; fibrinogen may decrease), improvement of blood flow in affected areas (measurable by Doppler ultrasound if assessed), and reduction of the sensation of "thick blood." After the initial aggressive treatment cycle, treatment can be transitioned to a reduced maintenance dose (20 mg once or twice daily) for recurrence prevention, or intermittent use (4 weeks on, 2 weeks off) for long-term maintenance in high-risk individuals. CRITICAL MONITORING : Perform a complete coagulation panel (PT/INR, PTT, D-dimer, fibrinogen, platelet count) before initiation, at 4 weeks, and at 8 weeks to confirm that coagulation is normalizing without dangerous over-anticoagulation. INTERACTIONS : Lumbrokinase should NOT be combined with pharmaceutical anticoagulants (warfarin, heparin, DOACs such as rivaroxaban/apixaban) without close medical supervision due to an additive risk of bleeding. If the patient is on anticoagulants, the transition should be carefully coordinated with a physician.
PILLAR 2: Biological Cleaning and Demolition Team
Serrapeptase
• Dosage : As a proteolytic enzyme derived from silkworms that acts as a "biological vacuum cleaner" by removing biofilm (a protective matrix built by bacteria/pathogens), old scar tissue, and fibrin that shouldn't be there, Serrapeptase complements Lumbrokinase by attacking clots from a different angle and clearing away debris left after dissolution. In the context of thrombosis where clearance of persistent fibrin and reduction of vascular inflammation are required, a dose of 80,000-120,000 SPU (Serratiopeptidase Units) per administration is recommended. For moderate dissolution and general maintenance, 80,000 SPU twice daily may be appropriate. For aggressive clearance of established clots, significant biofilm, or severe vascular inflammation, 120,000 SPU two or three times daily provides more pronounced proteolytic activity.
• Administration frequency : Serrapeptase is administered orally in enteric-coated capsules, typically two or three times daily on a strictly fasted diet (same critical requirements as lumbrokinase – 60+ minutes before a meal or 3+ hours post-meal). For simplicity, it can be coordinated with lumbrokinase doses: first dose in the morning on an empty stomach along with lumbrokinase, second dose mid-afternoon, and third dose at night before bed. Both enzymes can be taken simultaneously since they act synergistically, attacking fibrin through complementary mechanisms.
• Cycle Duration : Serrapeptase can be used for 8-12 week cycles, coinciding with the Lumbrokinase protocol, for complete clearance of fibrin, biofilm, and accumulated scar tissue. During use, the following are observed: reduction of vascular inflammation (swelling and redness decrease), elimination of biofilm that may protect clots from complete dissolution, improved circulation in areas with vascular scar tissue, and potential improvement of lymphatic drainage. After the intensive cycle, it can be reduced to a maintenance dose (80,000 SPU once daily) or used intermittently. SYNERGY WITH LUMBROKINASE : The combination is POWERFUL - Lumbrokinase activates plasmin for targeted fibrin dissolution, while Serrapeptase "cleans up the resulting mess" and attacks biofilm/scar tissue that could protect residual clots - together they accelerate resolution 2-3x compared to either alone.
Nattokinase
• Dosage : As a fibrinolytic enzyme derived from the Japanese fermented food natto (soybeans fermented with Bacillus subtilis), which, although slower than lumbrokinase, also supports the clot dissolution process by acting as an effective complement, nattokinase is valuable because it has a slightly different mechanism (it can dissolve fibrin directly AND activate the body's endogenous tissue plasminogen activator). In the context of supporting fibrinolysis and preventing the formation of new clots, a dose of 2,000-4,000 FU (Fibrinolytic Units) per administration is recommended. For prevention in individuals at moderate risk, 2,000 FU once or twice daily may be sufficient. For more aggressive clot dissolution support in combination with lumbrokinase/serrapeptase, 4,000 FU twice daily provides robust additional fibrinolytic activity.
• Administration frequency : Nattokinase is administered orally in capsules, typically once or twice daily on an empty stomach (morning and evening). It can be taken concurrently with lumbrokinase and serrapeptase as part of a "triple enzyme stack" for multi-vector attack against fibrin. The three-enzyme protocol creates a "perfect storm" of fibrinolysis, with each enzyme contributing in a complementary way.
• Cycle duration : Nattokinase can be used in 8-12 week cycles concurrently with other fibrinolytic enzymes, or for longer-term continuous use given its excellent safety profile and additional cardiovascular benefits (blood pressure reduction, improved lipid profile). Many cardiovascular prevention protocols use nattokinase indefinitely at maintenance doses (2,000 FU daily). SAFETY NOTE : Nattokinase contains vitamin K2 (particularly if natto is consumed as food), which may interfere with warfarin—warfarin users should avoid it or use it only under strict medical supervision with frequent INR monitoring.
PILLAR 3: Master of Vascular Repair
BPC-157
• Dosage : As an extraordinary "Body Protection Compound" peptide for blood vessel repair, acting as the "ultimate contractor" for endothelial cells (where clots form), BPC-157 repairs damaged endothelial lining (reducing the signal that triggers clot formation), reduces inflammation (especially in the portal vein of the liver—a high-risk area for thrombosis), and promotes angiogenesis (the creation of new blood vessels in case of obstruction to ensure oxygen perfusion to tissues). In the context of thrombosis where urgent repair of compromised endothelium and prevention of recurrent thrombosis are required, a dose of 500–1000 mcg per administration is recommended. For moderate vascular repair and prevention, 500 mcg twice daily may be appropriate. For aggressive repair after established thrombosis (DVT, portal vein thrombosis, embolic events), 1000 mcg twice a day or 500 mcg three times a day provides maximum saturation of endothelial reparative signaling.
• Frequency of administration : BPC-157 is administered by subcutaneous injection, typically two or three times daily (morning, afternoon, evening) for stable plasma levels and continuous 24/7 reparative signaling. For known localized thrombosis (e.g., DVT in the right leg), injection may be performed peri-lesionally (near the affected area within 5–10 cm if subcutaneously accessible) to maximize local concentration, although BPC-157 has potent systemic effects even when injected distally. For portal vein thrombosis or other inaccessible internal locations, abdominal subcutaneous injection is appropriate. Rotate injection sites appropriately.
• Duration of treatment : BPC-157 should be used during the active vascular repair phase, which typically lasts 8–12 weeks post-thrombotic event. During this period, dramatic improvements are observed in: endothelial integrity repair (reduction of pathological vascular permeability), reduction of local vascular inflammation (swelling, pain, and heat decrease), formation of collateral vessels (angiogenesis that bypasses obstructions, providing alternative blood flow routes), and normalization of function in affected organs (particularly the liver if portal vein thrombosis was present). After the intensive repair cycle, treatment can be transitioned to a reduced maintenance dose (250–500 mcg daily) for recurrence prevention, or intermittent use (4–6 weeks every 3–4 months) for long-term maintenance of vascular integrity in high-risk individuals.
PILLAR 4: Restoration of Vascular Elasticity and Demolition of Fibrosis
TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4)
• Dosage : As a critical peptide for dismantling scar tissue/fibrosis that clots frequently leave behind (compromising the elastic function of blood vessels) and restoring vascular flexibility vital to a healthy vascular system by regulating actin in the vascular wall (crucial for cell movement to injured areas), TB-500 is essential in the post-thrombotic recovery phase. In the context of post-clot vascular restoration where fibrosis reversal and improved elasticity are required, a biphasic protocol is recommended: Loading phase (first 4 weeks): 5 mg once a week. Maintenance phase (weeks 5+): 2.5 mg once a week or every two weeks.
• Administration frequency : TB-500 is administered by subcutaneous or intramuscular injection following the described biphasic protocol. Administer weekly or biweekly (its long half-life allows for this), on any fixed day of the week, preferably at night before bedtime. Injection can be SC (abdomen, thighs) or deep IM (buttocks, lateral thigh). TB-500 has predominantly systemic effects, therefore the injection site is flexible.
• Cycle duration : TB-500 is typically used in 8-12 week cycles (weeks 1-4 loading phase, 5 mg weekly; weeks 5-12 maintenance phase, 2.5 mg weekly or bi-weekly) for complete restoration of vascular elasticity and reversal of post-thrombotic fibrosis. During the cycle, the following are observed: dramatic improvement in vascular flexibility (vessels regain appropriate vasodilation/vasoconstriction capacity), reduction of scar tissue in vascular walls (measurable by vascular imaging studies if performed), improvement in overall circulation (particularly in the extremities if DVT was previously present), and a reduced risk of restenosis. After the cycle, a 6-8 week break is recommended. For long-term vascular recovery, cycles may be repeated 2-3 times per year. SYNERGY WITH BPC-157 : The combination of BPC-157 (endothelial repair) + TB-500 (restoration of elasticity and reversal of fibrosis) is POWERFUL SYNERGISTIC - BPC repairs "lining" while TB-500 restores "elastic structure" of vessels - together they rebuild complete vascular architecture.
PILLAR 5: Vascular Anti-inflammatory and Hair Regenerator
GHK-Cu (Copper Peptide)
• Dosage : As a potent anti-inflammatory peptide that massively increases Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF – which supports nitric oxide for vasodilation) and regenerates small networks of damaged or missing blood vessels (especially important in the gut/liver where oxygen perfusion is critical), GHK-Cu acts as an "adamantium armor," protecting the entire vascular system. In the context of thrombosis, where reduction of vascular inflammation and regeneration of compromised microcirculation are required, a dose of 200–300 mcg per administration is recommended. For moderate vascular support, 200 mcg daily may be sufficient. For aggressive post-thrombosis vascular regeneration with compromised microcirculation, 300 mcg daily or 200 mcg twice daily provides more robust stimulation of VEGF and angiogenesis.
• Frequency of administration : GHK-Cu is administered by subcutaneous injection, typically once daily (200–300 mcg) or twice daily (200 mcg each time) if maximum saturation is required. Morning administration is common, although specific timing is less critical than consistency. Subcutaneous injection at any standard site; rotate appropriately.
• Cycle duration : GHK-Cu can be used in 8-12 week cycles as a phase of vascular regeneration and intensive inflammation reduction. During this period, the following are observed: a dramatic reduction in vascular inflammatory markers, capillary regeneration in areas affected by thrombosis (improving tissue perfusion), increased nitric oxide production (improving vasodilation and blood flow), and potential improvement in the function of organs that suffered ischemia due to thrombosis. After the cycle, a 4-8 week break is recommended. For long-term vascular protection, cycles can be repeated 2-3 times per year.
PILLAR 6: Endothelial Tissue Regeneration Accelerator
MK-677 (Ibutamoren)
• Dosage : As a growth hormone secretagogue that stimulates the body to produce more endogenous GH/IGF-1 (accelerating tissue regeneration to optimal levels without stressing the system), MK-677 is essential for the recovery of endothelial cells, hepatocytes (critical liver cells post-portal vein thrombosis), and vascular smooth muscle, with a very high return on investment in recovery. In the context of post-thrombotic vascular regeneration where accelerated endothelial healing and recovery of compromised organs are required, a dosage of 12.5–25 mg daily is recommended. For women or sensitive users, 12.5 mg daily may be appropriate. For men or more aggressive regeneration, 25 mg daily provides a more robust elevation of GH/IGF-1.
• Administration frequency : MK-677 is administered orally, once daily. CRITICAL TIMING : Administer at night, 30-60 minutes before bedtime (takes advantage of the natural GH peak during sleep + may cause mild drowsiness beneficial for inducing sleep + increased appetite during sleep). It can be taken with or without food, although many users prefer to take it without food to minimize insulin resistance.
• Cycle Duration : MK-677 can be used in 12-16 week cycles as an acceleration phase for vascular and tissue regeneration. During use, the following are observed: a dramatic increase in serum IGF-1 (typically a 40-80% increase), accelerated healing of damaged endothelium, improved liver function (particularly important if there was portal vein thrombosis with hepatocyte damage), improved sleep quality (increased deep sleep where most repair occurs), and potential improvement in body composition. MONITORING : Fasting glucose should be monitored (MK-677 may cause mild insulin resistance - if glucose increases >10 mg/dL persistently, reduce dose or discontinue). After the cycle, a 4-6 week break is recommended. For long-term vascular regeneration, cycles may be repeated.
PILLAR 7: Liver Protection and Cellular Detoxification
TUDCA (Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid)
• Dosage : As a vital conjugated bile acid for protecting the liver (one of the organs most affected by thrombotic events such as portal vein thrombosis) by supporting bile flow, reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress in the liver, and improving hepatocyte function, TUDCA is essential for "saving the liver from the devastating consequences of thrombosis and oxidative stress." In the context of post-thrombosis liver protection or prevention of liver damage during the use of multiple compounds, a dose of 500-1000 mg daily is recommended. For moderate liver protection, 500 mg daily may be sufficient. For aggressive protection following portal vein thrombosis or compromised liver function, 1000 mg daily (divided into two 500 mg doses) provides more robust support.
• Frequency of administration : TUDCA is administered orally, typically once or twice daily with meals (taking it with a fatty meal improves absorption of this bile acid). Common protocol: 500 mg with breakfast + 500 mg with dinner if using a 1000 mg daily dose, or 500 mg once daily with a main meal.
• Cycle duration : TUDCA can be used continuously throughout the entire post-thrombotic recovery protocol (12-16+ weeks) and beyond, given its excellent safety profile. During use, the following are observed: improved liver enzymes (ALT, AST, and GGT normalize if elevated), improved bile flow (reduction of cholestasis, if present), protection of hepatocytes against oxidative stress and apoptosis, and improved overall liver function. For long-term liver protection, TUDCA can be used indefinitely or in 12-week on, 4-week off cycles.
NAC (N-Acetylcysteine)
• Dosage : As a precursor to glutathione (the body's main antioxidant) that increases glutathione production, protecting the liver and blood from oxidative stress and an overactive immune system, NAC is critical for cellular detoxification during thrombosis recovery. In the context of antioxidant protection and liver support, a dose of 1200–1800 mg daily is recommended. For moderate antioxidant support, 1200 mg daily (600 mg twice daily) may be appropriate. For aggressive detoxification and robust liver protection, 1800 mg daily (600 mg three times daily) provides maximum glutathione elevation.
• Frequency of administration : NAC is administered orally, typically TWO or THREE times a day with meals (it may cause GI upset if taken on an empty stomach). Common protocol: 600 mg with breakfast, 600 mg with lunch, 600 mg with dinner if using a daily dose of 1800 mg.
• Cycle duration : NAC can be used continuously throughout the entire protocol (12-16+ weeks) and indefinitely long-term given its excellent safety profile. During use, the following are observed: increased intracellular glutathione (measurable in red blood cells if assessed), protection of hepatocytes against toxicity, improved pulmonary function (NAC is mucolytic), and reduced systemic oxidative stress. NAC is one of the few compounds that can be used permanently without the need for cycling.
PILLAR 8: Vascular Anti-Aging Genetic Reset
Epitalon
• Dosage : As a tetrapeptide "massive genetic reset button" that prevents recurrent clot formation by addressing telomere shortening and mitochondrial dysfunction (key factors in aging and predisposition to clotting), acting at the genetic level to reverse vascular system aging and restore optimal function ("turning off the vascular aging switch, making it operate like a younger system"), Epitalon is a unique component for long-term prevention. In the context of recurrent thrombosis prevention and vascular rejuvenation, the characteristic Epitalon protocol is recommended: 10 mg daily for 10-20 consecutive days as a deep "reprogramming" cycle.
• Frequency of administration : Epitalon is administered by subcutaneous injection once daily, preferably at night (1-2 hours before sleep), during the concentrated 10-20 day period of the active cycle. Absolute consistency at night optimizes effects. Rotate injection sites appropriately.
• Cycle Duration : The Epitalon protocol consists of an intensive 10-20 consecutive days of daily administration at 10 mg per dose, followed by an EXTREMELY long break of 4-6 MONTHS before repeating. This unique structure is based on the fact that Epitalon induces LASTING changes in: telomerase activity (telomere elongation that protects against vascular senescence), mitochondrial function (improved energy production in endothelial cells), and normalization of pineal gland function (regulating circadian rhythms that influence coagulation). For long-term thrombosis prevention, 10-20 day cycles performed twice a year (every 6 months) provide regular "pulses" of vascular anti-aging protection.
COMPLETE INTEGRATED PROTOCOL: Strategic Implementation by Phases
PHASE 1: DISSOLUTION AND INTENSIVE REPAIR (Weeks 1-8)
Objective : To aggressively dissolve existing clots, initiate endothelial repair, and protect affected organs.
Complete Daily Protocol :
UPON WAKING (6-8 AM - STRICT FASTING) :
- Lumbrokinase : 40 mg (2 capsules) subcutaneous
- Serrapeptase : 120,000 SPU (1-2 capsules)
- Nattokinase : 4,000 FU (1 capsule)
- Wait at least 60 minutes before having breakfast.
WITH BREAKFAST :
- TUDCA : 500 mg
- NAC : 600 mg
MID-AFTERNOON (3-4 PM - FASTING between meals) :
- Lumbrokinase : 40 mg
- Serrapeptase : 120,000 SPU
- Nattokinase : 4,000 FU (optional if used only 2x/day)
WITH LUNCH :
- NAC : 600 mg
AFTERNOON (5-6 PM) :
- BPC-157 : 500-1000 mcg subcutaneous
- GHK-Cu : 200-300 mcg subcutaneous
WITH DINNER :
- TUDCA : 500 mg
- NAC : 600 mg
NIGHT (9-10 PM - 3+ hours post-dinner FASTING) :
- Lumbrokinase : 40 mg
- Serrapeptase : 120,000 SPU
- BPC-157 : 500-1000 mcg subcutaneous
- MK-677 : 12.5-25 mg orally 30-60 min before bedtime
SUNDAY NIGHT (Once a week) :
- TB-500 : 5 mg subcutaneously or IM (weeks 1-4 loading phase)
DAYS 1-20 OF THE FIRST MONTH :
- Epitalon : 10 mg subcutaneously at night (only for the first 10-20 days, then DO NOT repeat until 6 months later)
Non-Negotiable Fundamentals During Phase 1 :
- Hydration: 2.5-3 liters of water daily (well-hydrated blood flows better)
- Movement: Walk 20-30 min every 2-3 hours (to prevent venous stasis)
- Limb elevation: If DVT in legs, elevate above the heart for 15-20 min, 3-4 times/day
- Compression stockings: If DVT, wear 20-30 mmHg graduated stockings during the day
- Natural anticoagulant diet: Rich in omega-3 (fatty fish 3-4 times/week), garlic (1-2 raw cloves daily), turmeric (1-2 g with piperferin), ginger (fresh ginger tea), eliminate processed sugars/oils
- AVOID : Sitting/being immobile for >2 continuous hours, long flights without movement, dehydration
Critical Monitoring Weeks 2, 4, 8 :
- Complete blood count (platelets, hemoglobin)
- D-dimer (should gradually decrease)
- Fibrinogen (should normalize)
- PT/INR, PTT (confirm NO over-anticoagulation)
- Complete liver panel (ALT, AST, GGT, bilirubin)
- Doppler ultrasound of affected area (weeks 4 and 8 - assess clot resolution)
Expected Results Week 8 :
- D-dimer reduced 50-80% from baseline
- Symptoms of blood clots (swelling, pain, pressure) reduced 60-90%
- Ultrasound shows significant reduction or resolution of thrombus
- Liver enzymes normalized or improving
- Subjective sensation of improved "blood flow"
PHASE 2: CONSOLIDATION AND CONTINUOUS REPAIR (Weeks 9-12)
Objective : Consolidate clot dissolution, complete endothelial repair, transition to maintenance.
Protocol Adjustments :
Reduction of Fibrinolytic Enzymes :
- Lumbrokinase : Reduce to 20 mg twice daily (morning fasting + night)
- Serrapeptase : Reduce to 80,000 SPU twice daily
- Nattokinase : Maintain 2,000-4,000 FU 1-2x/day
Continue Vascular Repair :
- BPC-157 : Maintain 500 mcg twice daily or reduce to once daily if excellent improvement is seen.
- TB-500 : Transition to maintenance phase 2.5 mg once a week (weeks 9-12)
- GHK-Cu : Continue 200-300 mcg daily
- MK-677 : Continue 12.5-25 mg nightly
Maintain Liver Protection :
- TUDCA : Continue 500-1000 mg daily
- NAC : Continue 1200-1800 mg daily
Monitoring Week 12 :
- Full panel as week 8
- Final Doppler ultrasound (confirm resolution)
- If normalized D-dimer (<500 ng/mL) and ultrasound show complete resolution, transition to maintenance can be initiated.
PHASE 3: LONG-TERM MAINTENANCE AND PREVENTION (Month 4+)
Objective : To prevent recurrence, maintain vascular integrity, and provide continuous protection.
Simplified Maintenance Protocol :
Diary :
- Nattokinase : 2,000 FU 1x/day on an empty stomach in the morning (continuous mild natural anticoagulant)
- NAC : 600 mg twice daily with meals (basic antioxidant support)
- Omega-3 : 3-4g EPA/DHA daily (anti-inflammatory, natural anticoagulant)
Intermittent (Boost cycles every 3-4 months) :
- Lumbrokinase : 20 mg twice daily for 4 weeks (preventive fibrin clearance)
- BPC-157 : 250-500 mcg daily x 4 weeks (maintenance of endothelial integrity)
- GHK-Cu : 200 mcg daily x 8 weeks (reduction of vascular inflammation)
- TUDCA : 500 mg daily continuously if liver function is compromised, or 8-week cycles every 4 months
Every 6 Months :
- Epitalon : 10-20 day cycle (vascular anti-aging reprogramming)
- TB-500 : 8-week cycle (restoration of vascular elasticity)
Permanent Foundations :
- Optimal hydration
- Regular movement (avoid sedentary lifestyle)
- Natural anticoagulant diet
- Inflammation management
POST-VACCINATION CONSIDERATIONS: Spike Protein
Background : Spike protein from mRNA-based vaccines has been implicated in: disruption of endothelial function, microclot formation, increased platelet activation, and reduced mitochondrial integrity.
Specific Protocol for Post-Vaccination Syndrome with Coagulation :
Triple Enzyme Stack (Critical for Disseminated Microclots) :
- Lumbrokinase + Serrapeptase + Nattokinase at FULL doses for 12-16 weeks (not 8)
- These dissolve fibrin from microclots without compromising natural emergency coagulation
Complete "Wolverine Protocol" (Total Vascular Reconstruction) :
- BPC-157 + TB-500 + GHK-Cu for 12-16 weeks
- They rebuild vasculature, expand microvessels, and reduce massive systemic inflammation.
Cellular Recovery Acceleration :
- MK-677 + Epitalon
- They improve cell signaling, repair genetic damage (telomeres), and restore mitochondrial function.
Intensive Oxidative Protection :
- High dose NAC (1800 mg daily)
- Vitamin C (1000-2000 mg daily)
- Quercetin (500 mg 2x/day - inhibits spike protein entry into cells)
- Zinc (30-50 mg daily)
Duration : Minimum 16 weeks, evaluate symptoms and markers before reducing.
COMPREHENSIVE MONITORING AND BIOMARKERS
Coagulation Panel (Every 4 Weeks During Active Phase) :
- D-dimer : Target <500 ng/mL (reflects fibrin degradation - should DECREASE)
- Fibrinogen : Target 200-400 mg/dL (normal range)
- PT/INR : Target 0.9-1.1 (confirm NO over-anticoagulation)
- PTT : Target normal range 25-35 sec
- Platelet count : Target 150,000-400,000/μL
- Complete blood count : Monitor hemoglobin (rule out occult bleeding)
Liver Panel (Every 4 Weeks) :
- ALT, AST, GGT, alkaline phosphatase, total/direct bilirubin
- Objective: Gradual normalization if levels were elevated
Imaging Studies :
- Doppler ultrasound : Baseline, week 4, week 8, week 12
- Evaluates: Thrombus size, blood flow, collateral formation
- Objective: Progressive resolution until complete
Inflammatory Markers :
- hsCRP: Target <1 mg/L
- Homocysteine: Target <10 μmol/L (elevated = thrombotic risk)
CRITICAL WARNINGS
Absolute Contraindications :
- Bleeding disorders (hemophilia, von Willebrand disease)
- Scheduled surgery <2 weeks (discontinue fibrinolytic enzymes 7 days pre-op)
- Active bleeding
- recent hemorrhagic stroke (<3 months)
- Active bleeding peptic ulcer
Critical Drug Interactions :
- Anticoagulants (warfarin, heparin, DOACs) + Lumbrokinase/Nattokinase: SEVERE RISK OF BLEEDING
- Transition from anticoagulants to a natural protocol MUST be medically supervised
- Antiplatelet agents (aspirin, clopidogrel) + enzymes: Caution, strict monitoring
- NSAIDs + protocol: Increase risk of GI bleeding
Warning Signs (Discontinue and Seek Immediate Attention) :
- Bleeding that does not stop (nosebleeds, gum bleeding, large spontaneous bruises)
- Blood in urine or stool (tarry black)
- Sudden severe headache (rule out intracranial hemorrhage)
- Severe abdominal pain (rule out internal bleeding)
Special Population :
- Pregnancy/Breastfeeding: AVOID (safety not established)
- Elderly patients >75 years: Start with 50% of the dose, titrate conservatively
CONCLUSION: REPROGRAMMING VASCULAR HEALTH
Blood clots are NOT an inevitable fate - they are a sign of a compromised vascular system that CAN be repaired.
This protocol is NOT symptom management - it is DEEP CELLULAR REBUILDING.
The 8 pillars tackle the problem from ALL angles:
Dissolution : Lumbrokinase + Serrapeptase + Nattokinase eliminate fibrin. Repair : BPC-157 + TB-500 rebuild endothelium and elasticity. Regeneration : GHK-Cu + MK-677 regenerate vasculature and tissues. Protection : TUDCA + NAC protect the liver and cells from oxidative stress. Reset : Epitalon reprograms the vascular system at the genetic level.
Result: Vascular system that does NOT form pathological clots, that repairs itself efficiently, that maintains optimal flow.
Don't wait.
Don't ignore the signs.
Act URGENTLY.
Your biology responds to the right signals.
Give him the signs.
Rebuild your vascular system.
Claim your health.