Collection:
Balance of the gut microbiota
Indicated to promote a balanced intestinal microbiome, supporting the diversity and abundance of beneficial bacteria, and optimizing the digestive, immune and metabolic function of the body. They contribute to: Promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria : They stimulate the proliferation...
Indicated to promote a balanced intestinal microbiome, supporting the diversity and abundance of beneficial bacteria, and optimizing the digestive, immune and metabolic function of the body.
They contribute to:
- Promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria : They stimulate the proliferation of strains such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium by providing prebiotics and specific nutrients.
- Reduction of pathogenic bacteria : They regulate the microbial balance by inhibiting the growth of harmful microorganisms that affect intestinal health.
- Strengthening the intestinal barrier : They improve the integrity of the intestinal epithelium, reducing permeability and preventing bacterial translocation.
- Production of healthy metabolites : They promote the synthesis of short-chain fatty acids (butyrate, propionate and acetate), essential for colon health and inflammatory regulation.
- Modulation of the immune system : They regulate the activity of immune cells through signals derived from the microbiome, promoting a balanced immune response.
- Reduction of systemic inflammation : They decrease the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines associated with an imbalance in the microbiota.
- Improved digestion and nutrient absorption : They optimize the breakdown of food and the assimilation of essential vitamins and minerals.
- Regulation of the gut-brain axis : They influence the production of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, positively impacting mood and cognitive function.
-
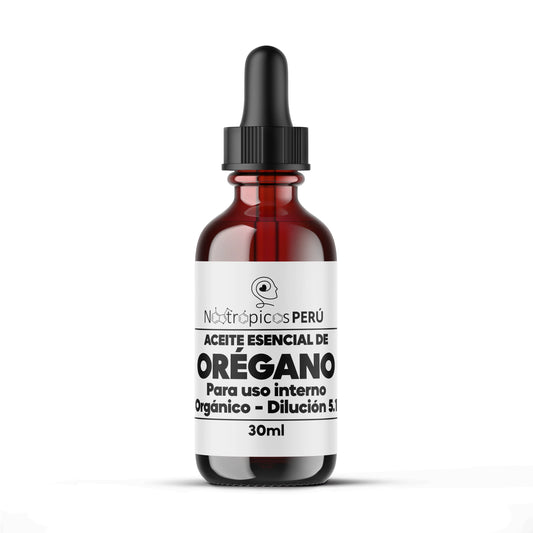
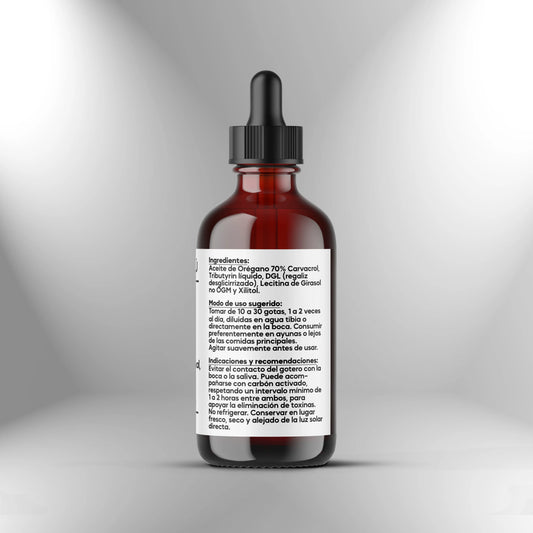
Oregano Oil 5.1 (70% Carvacrol) - 30ml
Regular price S/. 90.00Sale price S/. 90.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
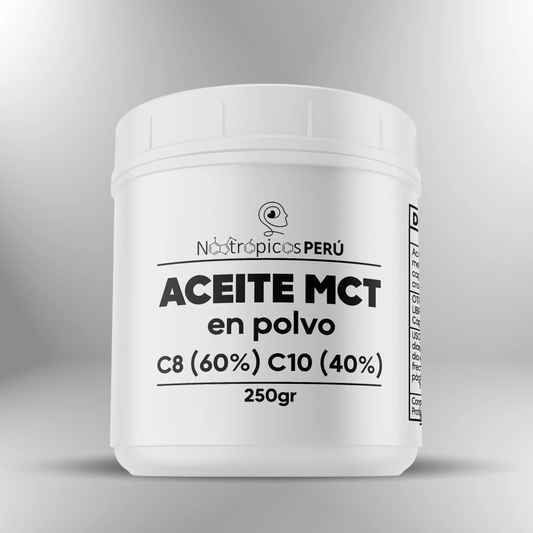
MCT Oil Powder C8 (60%) C10 (40%) ► 250g
Regular price S/. 160.00Sale price S/. 160.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
Pure MCT Oil (60% C8 - 40% C10) - 250ml
Regular price S/. 280.00Sale price S/. 280.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
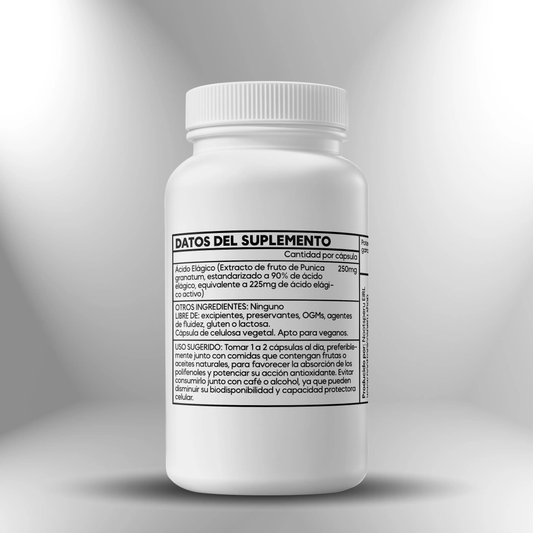
Ellagic Acid 90% (Pomegranate Extract) 250mg - 100 Capsules
Regular price S/. 140.00Sale price S/. 140.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
Resistant starch (prebiotic fiber from green banana) 250g
Regular price S/. 80.00Sale price S/. 80.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
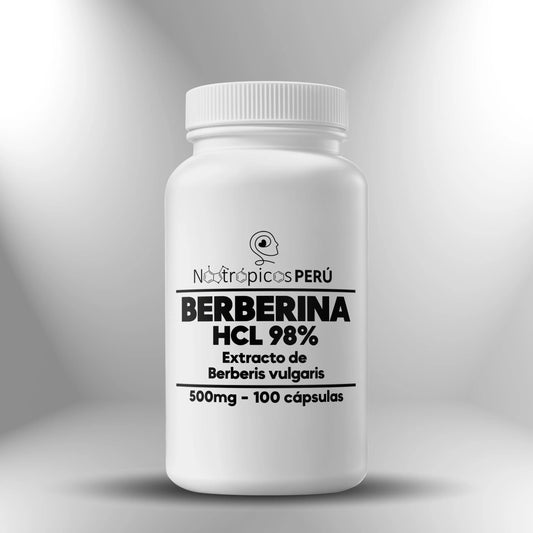
Berberine HCL 98% 500 mg - 100 capsules
Regular price S/. 190.00Sale price S/. 190.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
Liposomal Berberine 550mg - 100 capsules
Regular price S/. 210.00Sale price S/. 210.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
Bifidobacterium lactis Bl-04 (Probiotic) 6 billion per cap. ► 100 capsules
Regular price S/. 130.00Sale price S/. 130.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
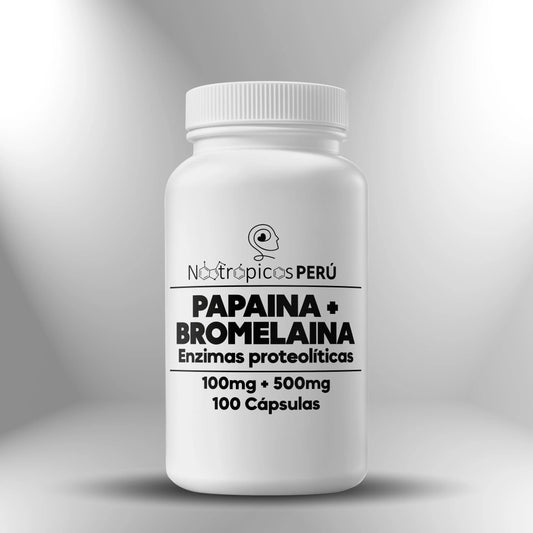
Bromelain + Papain (500mg + 100mg) - 50 capsules
Regular price S/. 100.00Sale price S/. 100.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
Sodium butyrate (Butyric Acid) 600mg ► 100 capsules
5.0Regular price S/. 100.00Sale price S/. 100.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
C15 (Pentadecanoic Acid) 100mg - 50 capsules
Regular price S/. 180.00Sale price S/. 180.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
C3G Longevix (cyanidin 3-glucoside) 500 mg - 50 capsules
Regular price S/. 150.00Sale price S/. 150.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
Freeze-dried beef foot broth (Collagen I, II and III) 700mg - 120 capsules
Regular price S/. 80.00Sale price S/. 80.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
Zinc carnosine (Polaprezinc) 75mg - 2 presentations
Regular price From S/. 60.00Sale price From S/. 60.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
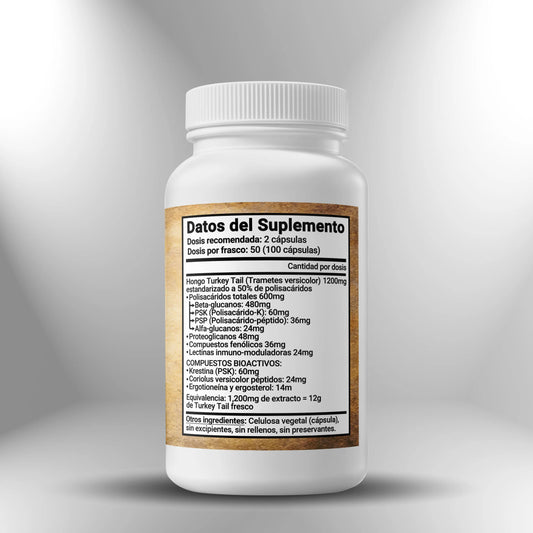
Turkey Tail (50% polysaccharide extract) 600 mg ►100 capsules
Regular price S/. 120.00Sale price S/. 120.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
B-Active Complex (Activated B Vitamins) - 100 capsules
5.0Regular price S/. 140.00Sale price S/. 140.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
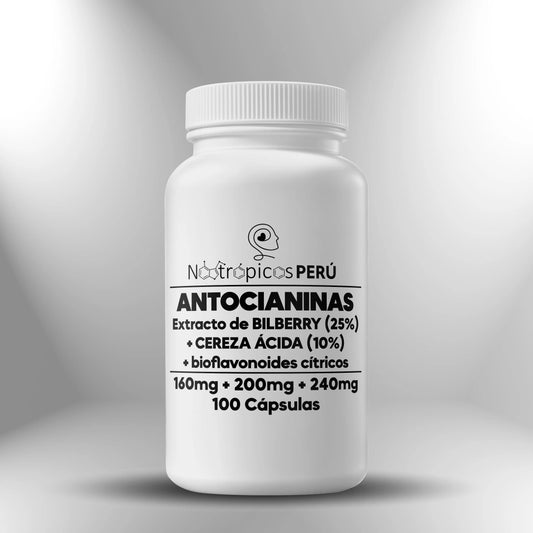
Anthocyanin Complex (600mg) - 100 capsules
Regular price S/. 120.00Sale price S/. 120.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
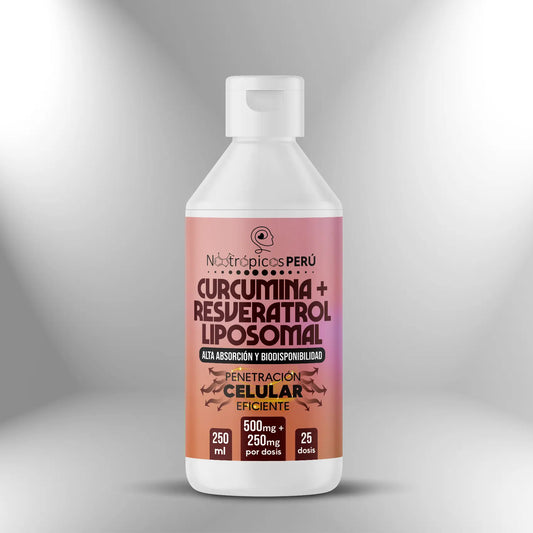
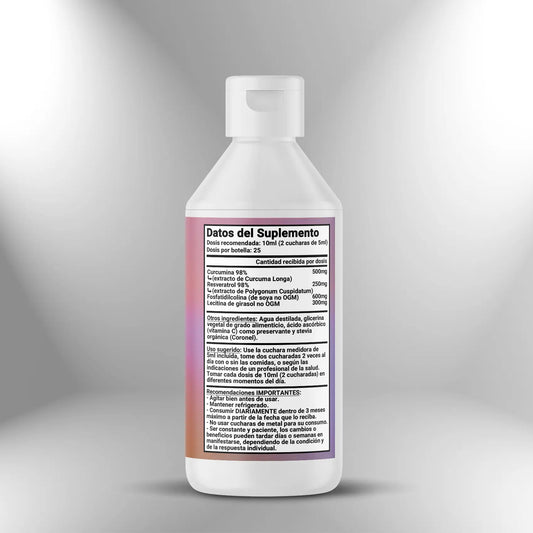
Liposomal Curcumin + Resveratrol (500mg + 250mg x 10ml) - 250ml (25 doses)
Regular price S/. 250.00Sale price S/. 250.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
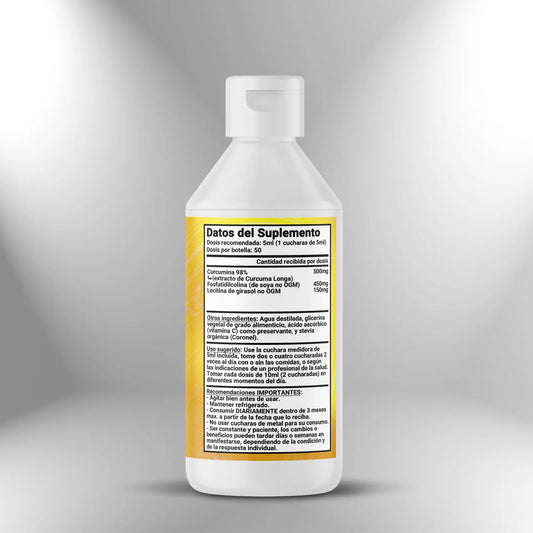
Curcumin 98% + Piperine 600mg - 100 capsules
Regular price S/. 190.00Sale price S/. 190.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
Liposomal Curcumin (500mg x 5ml) - 250ml
Regular price S/. 210.00Sale price S/. 210.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
Dysbiosis Control (restores microbial balance) - 50ml
Regular price S/. 90.00Sale price S/. 90.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
Spermidine (Spermidine 98%) 1mg, 5mg and 10mg ► 100 capsules
Regular price From S/. 70.00Sale price From S/. 70.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
Fenbendazole 500 mg ► 100 capsules
Regular price S/. 160.00Sale price S/. 160.00 Regular priceUnit price / per -
FloraFuel (Prebiotic Formula) ► 250gr
Regular price S/. 140.00Sale price S/. 140.00 Regular priceUnit price / per